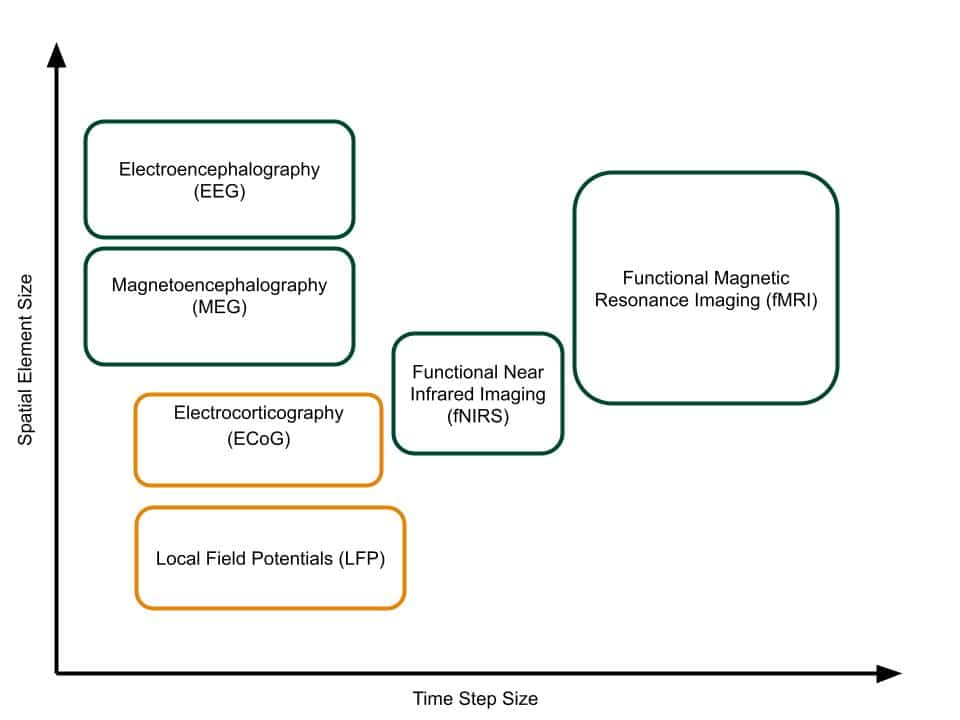
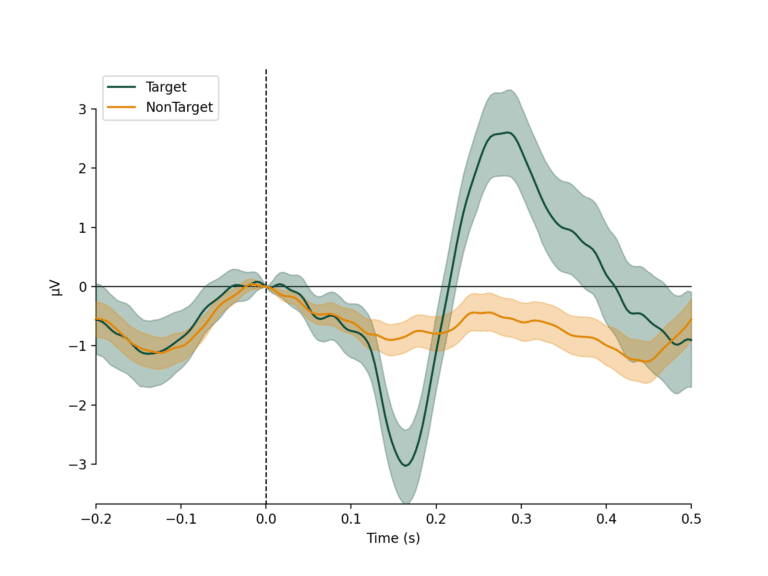
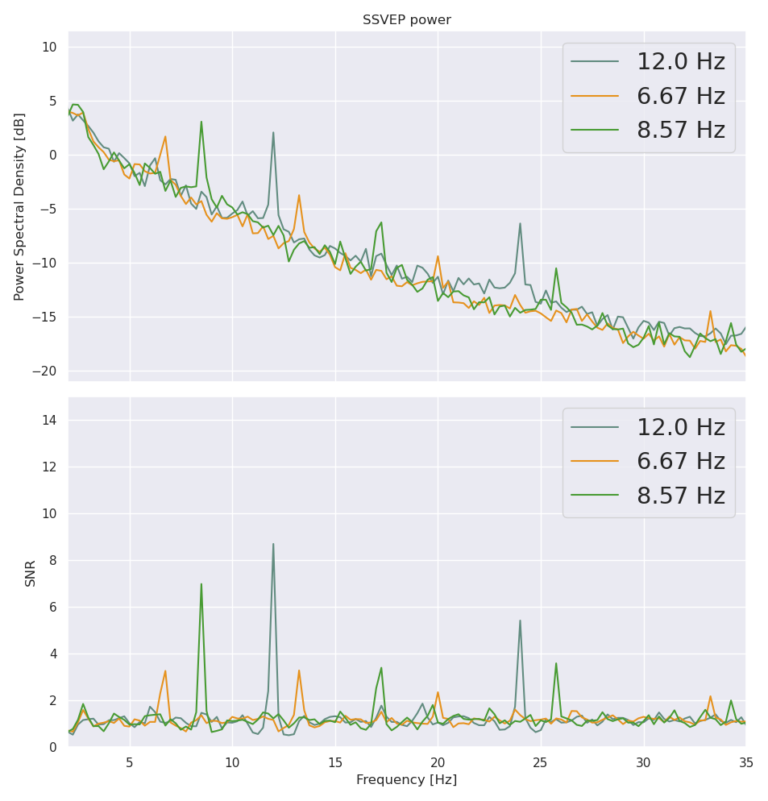
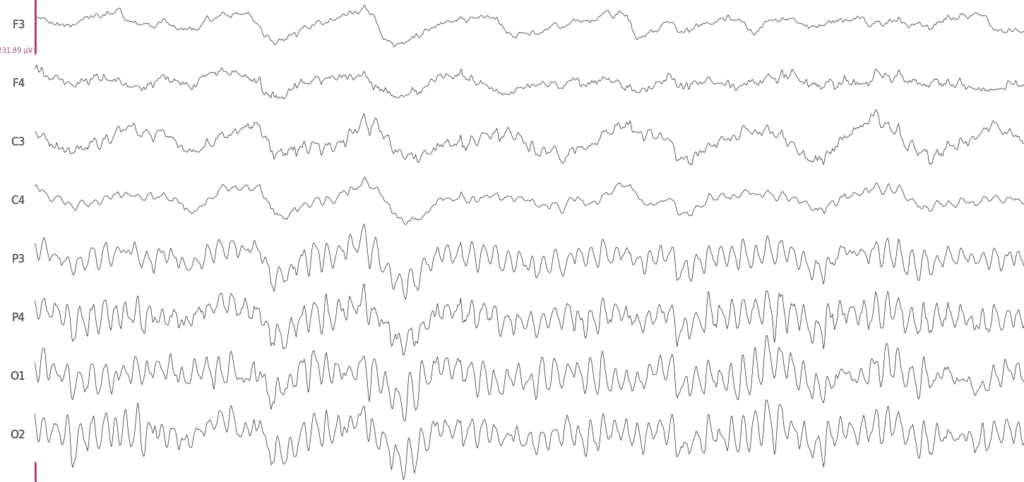
fNIRS technique observes the hemodynamic response of the brain by measuring the oxygenation level, which increases with elevated activation of local neuron populations. The temporal resolution of fNIRS is lesser than the EEG, however it can penetrate further through the skull and measure from the neuronal structures deeper within the brain. In addition, no contact or scalp preparation is needed for the measurements to be made, although the sensor placement stability or a person’s hair may have a significant influence on the quality of the measurements. The fNIRS devices are becoming more portable and in some cases it is also being combined with EEG sensors offering a versatile measurement system.